Important:If you are using a prerelease (Early Adopter) version of SQL Developer, and if you want to be able to continue to use this prerelease version after installing the official release kit, you must unzip the official release kit into a different directory than the one used for the prerelease version.If Oracle Database (Release 11 or later) is also installed, a version of SQL Developer is also included and is accessible through the menu system under Oracle. This version of SQL Developer is separate from any SQL Developer kit that you download and unzip on your own, so do not confuse the two, and do not unzip a kit over the SQL Developer files that are included with Oracle Database.
Note:If a Windows 64-bit SQL Developer kit that includes JDK 7 is available, you can download and install that on a Windows 64-bit system, and SQL Developer will use the embedded JDK that is provided with that kit.However, if you need or simply want to use a JDK on your Windows 64-bit system, you can install the JDK (if it is not already installed) and the Windows 32/64-bit SQL Developer kit, and SQL Developer will use the JDK that is installed on your system.If you do not need or want to install a suitable Java Development Kit (JDK 7 or later), go to step 3. Note:On Macintosh systems, a native Macintosh application in the form sqldeveloper xxx.tar.gz is provided. When it is expanded, it appears as a Macintosh application that can be put into the applications folder. If you choose to expand this file, it will replace any older sqldeveloper applications in that folder.To install and start SQL Developer, follow these steps:.Unzip the SQL Developer kit into a directory (folder) of your choice. (Ensure that the Use folder names option is checked when unzipping the kit.) This directory location will be referred to as.Unzipping the SQL Developer kit causes a directory named sqldeveloper to be created under the directory.
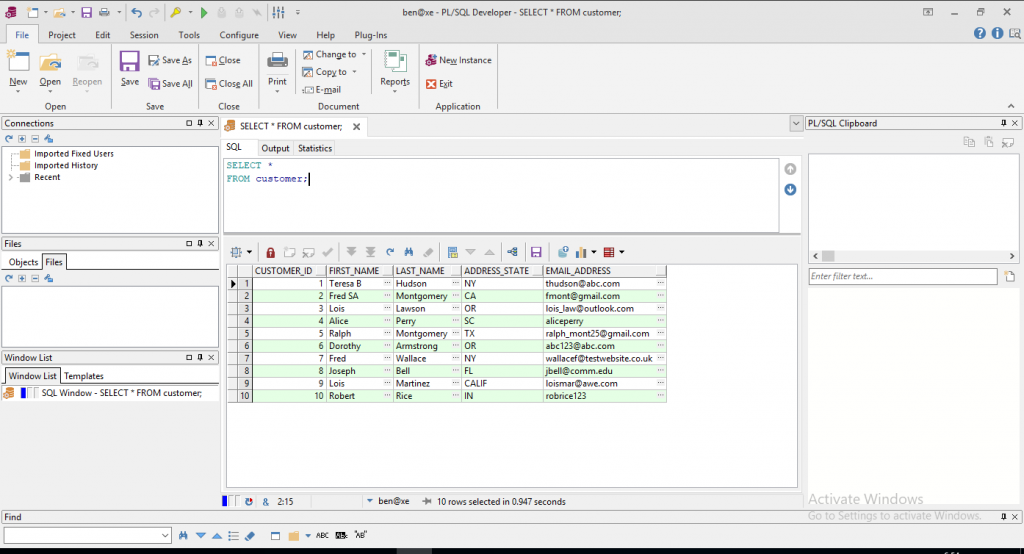
It also causes many files and directories to be placed in and under that directory.To start SQL Developer, go to the sqldeveloper directory under the directory, and run sh sqldeveloper.sh.After SQL Developer starts, you can connect to any database by right-clicking the Connections node in the Connections Navigator and selecting New Connection. Alternatively, if you have any exported connections (see or ), you can import these connections and use them.You can learn about SQL Developer by clicking Help, then Table of Contents, and reading the help topics under SQL Developer Concepts and Usage. 1.3 Migrating User Settings from a Previous ReleaseThe first time you start SQL Developer after installing it or after adding any extensions, you are asked if you want to migrate your user settings from a previous release. (This occurs regardless of whether there was a previous release on your system.)These settings refer to database connections, reports, and certain SQL Developer user preferences that you set in a previous version by clicking Tools and then Preferences. However, some user preferences are not saved, and you must respecify these using the new release.To migrate user settings from a previous SQL Developer release:.Unzip the kit for the current release so as to create a new sqldeveloper directory.When you start the SQL Developer current release, click Yes when asked if you want to migrate settings from a previous release.In the dialog box that is displayed, you can accept the default option to migrate the settings from the most recent SQL Developer installation. Or, if you want to migrate the settings from an earlier installation, you can click to show all builds and then select the desired one.See also.

1.4 Migrating Information from Previous ReleasesIf you have used a previous release of SQL Developer, you may want to preserve database connections that you have been using. To preserve database connections, save your existing database connections in an XML file. To save the connections, right-click the Connections node in the Connections Navigator and select Export Connections. After you complete the installation described in this guide, you can use those connections by right-clicking the Connections node in the Connections Navigator and selecting Import ConnectionsIf you want to use any user-defined reports or the SQL history from a previous version, see for information about where these are located. If you have user-defined reports and SQL history from Release 1.0, they are modified by any later SQL Developer release to a format that is different from and incompatible with Release 1.0.SQL Developer preferences (specified by clicking Tools and then Preferences) from a prerelease version of the current release cannot currently be saved and reused; you must respecify any desired preferences.
1.5 Location of User-Related InformationSQL Developer stores user-related information in several places, with the specific location depending on the operating system and certain environment specifications. User-related information includes user-defined reports, user-defined snippets, SQL Worksheet history, code templates, and SQL Developer user preferences. In most cases, your user-related information is stored outside the SQL Developer installation directory hierarchy, so that it is preserved if you delete that directory and install a new version.The user-related information is stored in or under the IDEUSERDIR environment variable location, if defined; otherwise as indicated in, which shows the typical default locations (under a directory or in a file) for specific types of resources on different operating systems.
(Note the period in the name of any directory named.sqldeveloper.). 1.7 Advanced Security for JDBC Connection to the DatabaseYou are encouraged to use Oracle Advanced Security to secure a JDBC connection to the database. Both the JDBC OCI and the JDBC Thin drivers support at least some of the Oracle Advanced Security features. If you are using the OCI driver, you can set relevant parameters in the same way that you would in any Oracle client setting. The JDBC Thin driver supports the Oracle Advanced Security features through a set of Java classes included with the JDBC classes in a Java Archive (JAR) file and supports security parameter settings through Java properties objects. Note:Unless otherwise indicated, the information is this section also applies to Data Modeler and Data Miner.To make the best use of our accessibility features, Oracle Corporation recommends the following minimum configuration:.Windows XP, Windows Vista.Java 7 Update 6Java 7 Update 6 includes the Java Access Bridge. For more information, including how to enable the Java Access Bridge, see:However, if you are using Java J2SE 1.6.024 or higher but before Java 7 Update 6, you must manually install Java Access Bridge 2.0.2 after you install the screen reader (if it is not already installed).
Download Java Access Bridge for Windows version 2.0.2. The file you will download is accessbridge-202-fcs-bin-b06.zip. 1.9.1 If You Need to Install Java Access BridgeIf you are using Java J2SE 1.6.024 or later but before Java 7 Update 6, you must manually install Java Access Bridge 2.0.2 after you install the screen reader (if it is not already installed).Download Java Access Bridge for Windows version 2.0.2. The file you will download is accessbridge-202-fcs-bin-b06.zip. It is available from:.Refer to the Java Access Bridge documentation available from this website for more information about installation and the Java Access Bridge.Extract (unzip) the contents to a folder, for example, accessbridgehome.Install Java Access Bridge by running Install.exe from the installer folder.The installer first checks the JDK version for compatibility, then the Available Java virtual machines dialog displays.Click Search Disks.
Then select to search only the drive that contains the SQL Developer build and the JDK version in the program files directory (if it exists).The search process can take a long time on a large disk with many instances of JDK or SQL Developer, or when searching multiple disks. However, unless you complete an exhaustive search of your disk, Access Bridge will not be optimally configured, and will not be correctly installed to all of the Java VMs on your system.
Important:If you are using a prerelease (Early Adopter) version of SQL Developer, and if you want to be able to continue to use this prerelease version after installing the official release kit, you must unzip the official release kit into a different directory than the one used for the prerelease version.If Oracle Database (Release 11 or later) is also installed, a version of SQL Developer is also included and is accessible through the menu system under Oracle. This version of SQL Developer is separate from any SQL Developer kit that you download and unzip on your own, so do not confuse the two, and do not unzip a kit over the SQL Developer files that are included with Oracle Database. Note:If a Windows 64-bit SQL Developer kit that includes JDK 7 is available, you can download and install that on a Windows 64-bit system, and SQL Developer will use the embedded JDK that is provided with that kit.However, if you need or simply want to use a JDK on your Windows 64-bit system, you can install the JDK (if it is not already installed) and the Windows 32/64-bit SQL Developer kit, and SQL Developer will use the JDK that is installed on your system.If you do not need or want to install a suitable Java Development Kit (JDK 7 or later), go to step 3. Note:On Macintosh systems, a native Macintosh application in the form sqldeveloper xxx.tar.gz is provided. When it is expanded, it appears as a Macintosh application that can be put into the applications folder. If you choose to expand this file, it will replace any older sqldeveloper applications in that folder.To install and start SQL Developer, follow these steps:.Unzip the SQL Developer kit into a directory (folder) of your choice.
(Ensure that the Use folder names option is checked when unzipping the kit.) This directory location will be referred to as.Unzipping the SQL Developer kit causes a directory named sqldeveloper to be created under the directory. It also causes many files and directories to be placed in and under that directory.To start SQL Developer, go to the sqldeveloper directory under the directory, and run sh sqldeveloper.sh.After SQL Developer starts, you can connect to any database by right-clicking the Connections node in the Connections Navigator and selecting New Connection. Alternatively, if you have any exported connections (see or ), you can import these connections and use them.You can learn about SQL Developer by clicking Help, then Table of Contents, and reading the help topics under SQL Developer Concepts and Usage. 1.3 Migrating User Settings from a Previous ReleaseThe first time you start SQL Developer after installing it or after adding any extensions, you are asked if you want to migrate your user settings from a previous release. (This occurs regardless of whether there was a previous release on your system.)These settings refer to database connections, reports, and certain SQL Developer user preferences that you set in a previous version by clicking Tools and then Preferences. However, some user preferences are not saved, and you must respecify these using the new release.To migrate user settings from a previous SQL Developer release:.Unzip the kit for the current release so as to create a new sqldeveloper directory.When you start the SQL Developer current release, click Yes when asked if you want to migrate settings from a previous release.In the dialog box that is displayed, you can accept the default option to migrate the settings from the most recent SQL Developer installation.
Or, if you want to migrate the settings from an earlier installation, you can click to show all builds and then select the desired one.See also. 1.4 Migrating Information from Previous ReleasesIf you have used a previous release of SQL Developer, you may want to preserve database connections that you have been using. To preserve database connections, save your existing database connections in an XML file. To save the connections, right-click the Connections node in the Connections Navigator and select Export Connections.
After you complete the installation described in this guide, you can use those connections by right-clicking the Connections node in the Connections Navigator and selecting Import ConnectionsIf you want to use any user-defined reports or the SQL history from a previous version, see for information about where these are located. If you have user-defined reports and SQL history from Release 1.0, they are modified by any later SQL Developer release to a format that is different from and incompatible with Release 1.0.SQL Developer preferences (specified by clicking Tools and then Preferences) from a prerelease version of the current release cannot currently be saved and reused; you must respecify any desired preferences. 1.5 Location of User-Related InformationSQL Developer stores user-related information in several places, with the specific location depending on the operating system and certain environment specifications. User-related information includes user-defined reports, user-defined snippets, SQL Worksheet history, code templates, and SQL Developer user preferences. In most cases, your user-related information is stored outside the SQL Developer installation directory hierarchy, so that it is preserved if you delete that directory and install a new version.The user-related information is stored in or under the IDEUSERDIR environment variable location, if defined; otherwise as indicated in, which shows the typical default locations (under a directory or in a file) for specific types of resources on different operating systems. (Note the period in the name of any directory named.sqldeveloper.). 1.7 Advanced Security for JDBC Connection to the DatabaseYou are encouraged to use Oracle Advanced Security to secure a JDBC connection to the database.
Pl Sql Developer Download For Windows 7 64 Bit
Both the JDBC OCI and the JDBC Thin drivers support at least some of the Oracle Advanced Security features. If you are using the OCI driver, you can set relevant parameters in the same way that you would in any Oracle client setting. The JDBC Thin driver supports the Oracle Advanced Security features through a set of Java classes included with the JDBC classes in a Java Archive (JAR) file and supports security parameter settings through Java properties objects. Note:Unless otherwise indicated, the information is this section also applies to Data Modeler and Data Miner.To make the best use of our accessibility features, Oracle Corporation recommends the following minimum configuration:.Windows XP, Windows Vista.Java 7 Update 6Java 7 Update 6 includes the Java Access Bridge. For more information, including how to enable the Java Access Bridge, see:However, if you are using Java J2SE 1.6.024 or higher but before Java 7 Update 6, you must manually install Java Access Bridge 2.0.2 after you install the screen reader (if it is not already installed). Download Java Access Bridge for Windows version 2.0.2.
The file you will download is accessbridge-202-fcs-bin-b06.zip. 1.9.1 If You Need to Install Java Access BridgeIf you are using Java J2SE 1.6.024 or later but before Java 7 Update 6, you must manually install Java Access Bridge 2.0.2 after you install the screen reader (if it is not already installed).Download Java Access Bridge for Windows version 2.0.2.
Free Software For Windows 7 64 Bit
The file you will download is accessbridge-202-fcs-bin-b06.zip. It is available from:.Refer to the Java Access Bridge documentation available from this website for more information about installation and the Java Access Bridge.Extract (unzip) the contents to a folder, for example, accessbridgehome.Install Java Access Bridge by running Install.exe from the installer folder.The installer first checks the JDK version for compatibility, then the Available Java virtual machines dialog displays.Click Search Disks. Then select to search only the drive that contains the SQL Developer build and the JDK version in the program files directory (if it exists).The search process can take a long time on a large disk with many instances of JDK or SQL Developer, or when searching multiple disks. However, unless you complete an exhaustive search of your disk, Access Bridge will not be optimally configured, and will not be correctly installed to all of the Java VMs on your system.